
These are temporary accounts, and they’ve already made it into the ‘Retained earnings’ section at this stage. Therefore, this sort of Trial balance mustn’t have any unnoticed temporary accounts. Moreover, the accountants make sure the equality between debit and credit. Hence, they can record the additional transactions for the next period. The next step after preparing an Adjusted Trial Balance would be the closing process.
Step-by-Step Guide to Preparing a Post-Closing Trial Balance
The fiscal health of a nation and its companies are linked. If a country expects higher debt-to-GDP ratios, companies might face tougher rules. This could change how they manage their money and affect investor profits. It shows why it’s key for S&P 500 or Dow Jones companies to keep their finances clear and sustainable.
Trial balance: Definition, purpose, and example
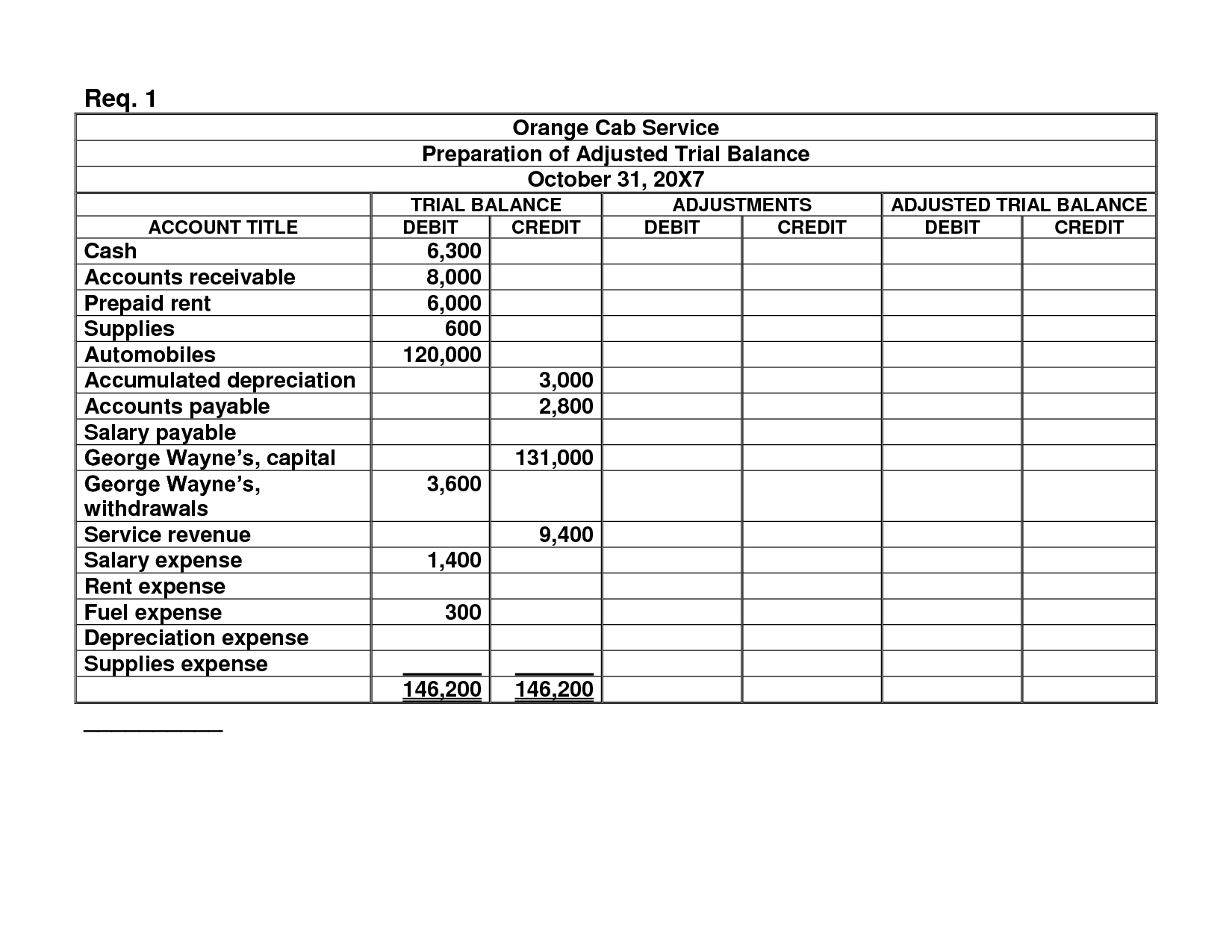
It’s basically a summary of the general ledger at the end of an accounting period after the closing entries have been made and the financial statements have been prepared. The purpose of this trial balance is to make sure that no more temporary account balances exist before the books are rolled forward into the next year. A post-closing trial balance is a list of balances of ledger accounts prepared after closing entries have been passed and posted to the ledger accounts. However, all the other accounts having non-negative balances are listed including the retained earnings account.
What are the key differences between pre-closing and post-closing trial balances?
As a result, temporary accounts do not have balances at the end of the accounting period and are not included in a post-closing trial balance. Business owners and accounting teams rely on the trial balance to create reliable financial statements. A trial balance ensures the accuracy of your accounting system and is just one of the many steps in the accounting cycle.
- By verifying the equality of debits and credits, the post-closing trial balance confirms that the accounts are ready for the next accounting period.
- The debit and credit amount columns will be summed and the totals should be identical.
- The post-closing trial balance is a crucial component of the accounting cycle, serving as the final step before a new accounting period begins.
- A post-closing trial balance is a list of balance sheet accounts with net-zero balances at the end of the reporting period.
- This important step ensures retained earnings on the books match those reported.
However, most businesses can streamline this cycle and skip tedious steps like posting transactions to the general ledger and creating a trial balance. Using accounting software like QuickBooks Online can do all these tasks for you behind the scenes. Trial balances come in three key types, with each serving a purpose to help create accurate financial statements. The biggest goal of a trial balance is to find accounting errors and transposition errors like switching digits. By highlighting these mistakes, the trial balance acts as an accuracy check for a business, mitigating the risk of inaccuracies before you generate final financial statements. A list of the accounts and their balances at the end of the accounting period after closing entries have been journalized and posted.
This also helps to ensure that all temporary accounts have been properly closed, which is essential to ensure that accounts will remain accurate during the next cycle. This balance sheet will help ensure that a company’s beginning balances are correct for the next accounting cycle. Without correct information on all transactions, you can’t really create financial statements for the period.
This is because only balance sheet accounts are have balances after closing entries have been made. After Paul’s Guitar Shop posted its closing journal entries in the previous example, it can prepare this post closing trial balance. Since only balance sheet accounts are listed on this trial balance, they are presented in balance sheet order starting with assets, liabilities, and ending with equity. On the bottom-most row, these balances will be totaled, and if everything has been performed correctly, then the value of credits and debits should be equal. Well, the most notable difference is that the post-closing type of Trial balance doesn’t account for losses, gains, revenues & expenses.
A trial balance is an internal report that itemizes the closing balance of each of your accounting accounts. It acts as an auditing tool, while a balance sheet is a formal financial statement. It’s one of the first lines of defense against accounting errors and a pivotal report within double-entry bookkeeping. Let’s look at what a trial balance is, how it works, the various types, and examples. The accounting cycle ends with the preparation of a post-closing trial balance. This trial balance lists the accounts and their adjusted balances after closing.
Closing entries move totals from temporary accounts to retained earnings. This updates the equity section of the balance sheet and records are 529 contributions tax deductible net income or loss right. They’re vital for correct financial statements, affecting income and retained earnings statements.
This step is key in making sure the ledger shows permanent accounts correctly. Adjusted trial balance – This is prepared after adjusting entries are made and posted. Its purpose is to test the equality between debits and credits after adjusting entries are prepared. It is also the basis in preparing the financial statements. The post-closing trial balance is an essential tool in the accounting cycle, providing a final check on the accuracy and completeness of the financial records. By ensuring that all temporary accounts are closed and permanent accounts are balanced, the post-closing trial balance prepares the accounting system for the next period’s transactions.